Ext JS vs. Generic UI Components: Which Is Right for Your Enterprise Project?
Get a summary of this article:
Enterprise web applications are increasingly complex, requiring rich user interfaces, scalable architecture, and robust data-handling performance. For businesses, choosing the right front-end solution is critical to meeting these demands effectively.
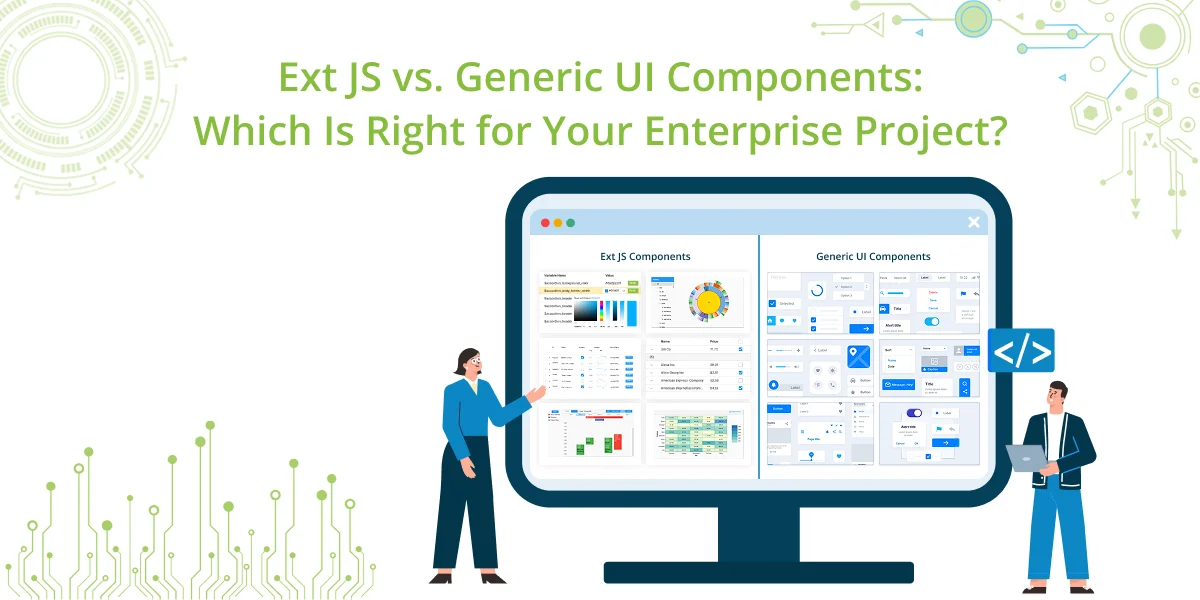
The dilemma often boils down to two choices: Ext JS, a complete front-end framework designed for enterprise-scale applications, or generic UI component libraries like Material UI, Bootstrap, Ant Design, and Kendo UI. Each option comes with distinct strengths and trade-offs.
This article explores the capabilities of both approaches, compares their features, and provides guidance to help enterprises make the right decision. Start building mission-critical enterprise applications today – try Ext JS, the leading enterprise JavaScript UI library, for free and create robust, scalable, and interactive web apps faster.
What Is Ext JS and How Does It Stand Out?
Ext JS is a full-fledged front-end framework specifically designed for building complex, data-intensive, enterprise-scale applications. It provides an all-in-one ecosystem for UI development, offering an unparalleled suite of tools and features.
Key Features of Ext JS:
1. Built-in Ecosystem
- Ext JS comes with 140+ pre-built UI components such as grids, charts, pivot tables, calendars, Gantt charts, and more.
- It includes a data handling package with built-in models, stores, and proxies for seamless data management.
- Architectural patterns like MVC (Model-View-Controller) and MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel) are supported, ensuring scalable and maintainable applications.
2. Enterprise-First Focus
- Ext JS handles large datasets efficiently with features like virtual rendering and infinite scrolling.
- Long-term support (LTS), detailed documentation, and professional support make it a reliable choice for enterprise-grade projects.
3. Theming and Customization
- The Sencha Themer allows developers to customize application themes without delving into complex CSS, enabling brand consistency across all platforms.
What Are Generic UI Component Libraries?
Generic UI libraries provide pre-styled components such as buttons, modals, forms, grids, and charts. Unlike Ext JS, these libraries require integration with frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue to build complete applications.
Popular Examples of Generic UI Libraries:
1. Material UI
- React-focused library based on Google’s Material Design principles.
- Excellent for modern, responsive web applications.
2. Bootstrap
- One of the most popular libraries for responsive design.
- Best suited for lightweight, simple apps or websites.
3. Ant Design
- A React-based library with rich components for dashboards and enterprise-focused interfaces.
4. Kendo UI
- A commercial library offering robust components with extensive documentation and support.
While generic UI libraries are highly flexible, they often rely on external tools for critical features like state management and data handling.
Also Read: MVVM Architecture Implementation in Ext JS Web Application
Key Differences: Ext JS vs. Generic UI Component Libraries
1. Component Ecosystem
- Ext JS: Offers a comprehensive ecosystem with 140+ pre-built components, making it ideal for enterprise-scale applications.
- Generic Libraries: Typically provide basic components (e.g., buttons, modals) and require third-party tools for advanced features.
2. Data Handling & State Management
- Ext JS: Includes built-in models, stores, and proxies for efficient data handling.
- Generic Libraries: Require external libraries like Redux or MobX to handle complex data workflows.
3. Performance for Enterprise-Scale Apps
- Ext JS: Excels with large datasets using virtual rendering, infinite scrolling, and lazy loading.
- Generic Libraries: Performance depends on the underlying framework and third-party integrations.
4. Consistency & Theming
- Ext JS: The Sencha Themer ensures consistent branding across apps.
- Generic Libraries: Libraries like Material UI and Ant Design provide robust theming systems.
5. Architecture & Scalability
- Ext JS: Supports MVC/MVVM patterns, making it easy to scale applications while maintaining structure.
- Generic Libraries: Require developers to define architecture, which can lead to inconsistencies in large projects.
6. Support & Longevity
- Ext JS: Offers enterprise-grade support, long-term updates, and a dedicated community.
- Generic Libraries: Primarily community-driven with varying levels of support and documentation.
Competitor Comparison Table
| Feature | Ext JS | Material UI | Bootstrap | Ant Design | Kendo UI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UI Components | 140+ (Grids, Charts, Trees) | Basic React components | Styling + layout | Rich React components | Enterprise-ready set |
| Data Handling | Built-in models, stores | External tools needed | External tools needed | External tools needed | Limited |
| Performance with Large Data | Excellent (virtual rendering) | Weak | Weak | Moderate | Good |
| Architecture | MVC/MVVM | React-based | None | React-based | Framework-based |
| Theming & Branding | Sencha Themer | Strong (Material Design) | Strong | Strong | Strong |
| Support | Enterprise-grade LTS | Community-driven | Community-driven | Community-driven | Commercial support |
| Best For | Large-scale, enterprise apps | React apps | Simple responsive apps | Enterprise dashboards | Mid-to-large projects |
Which Should You Choose for Your Enterprise Project?
Choose Ext JS if:
- You’re building data-intensive, mission-critical enterprise applications.
- You want an all-in-one ecosystem that eliminates the need for multiple libraries.
- Long-term scalability and enterprise-grade support are crucial for your project.
Choose Generic UI Components if:
- You’re developing smaller apps or MVPs.
- You prioritize lightweight and flexibility over enterprise-grade performance.
- Budget constraints favor free/open-source solutions.
Conclusion
Both Ext JS and generic UI libraries like Material UI, Bootstrap, and Ant Design have their strengths. The choice depends on your project’s scale, complexity, and long-term goals.
- Ext JS offers unparalleled robustness, scalability, and enterprise-level reliability, making it the best option for large-scale, data-heavy applications.
- Generic UI components are ideal for smaller, lightweight projects where simplicity and flexibility are key.
For enterprises looking to reduce technical debt, enhance scalability, and build mission-critical applications, Ext JS emerges as the clear winner.
FAQs
Which option offers better scalability for long-term projects?
Ext JS is better suited for scalable enterprise applications due to its built-in architecture and data-handling capabilities.
Can generic UI components be integrated into enterprise applications?
Yes, but they often require additional libraries and tools to handle enterprise-grade challenges effectively.
Is Ext JS suitable for modern web development trends like React or Angular integration?
Yes, Ext JS integrates seamlessly with frameworks like React (via ExtReact) and Angular (via ExtAngular).
Are generic UI components more future-proof than Ext JS?
Generic libraries rely on community adoption, which can vary. Ext JS offers long-term support and regular updates, ensuring reliability over time.
By understanding your project’s needs and goals, you can make an informed decision to choose the right front-end solution. Start building smarter today!
Try Ext JS free and create powerful apps faster. with hyperlink

The mobile application development landscape has undergone a profound transformation over the past decade. Organizations…

For Independent Software Vendors operating in competitive global markets, the user interface has evolved from…

The selection of a front end framework for enterprise applications remains one of the most…